1. GALAN electrode boiler;
2. Ball faucet;
3. Circulating pump ;
4. Filter;
5. Blow valve;
6. Expansion tank;
7. Automatic equipment;
8. Air-inlet duct;
9. Three-way valve;
10. Automatic equipment of the floor heating;
11. Floor heating circuit.
The connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler

The connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler to the radiator + the floor heating
The area of the heat-insulated floor should not exceed 30% of all heated area:
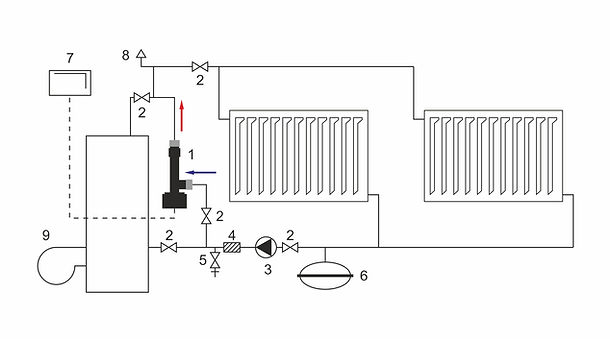
The connetion scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler with the ascension pipe
The connection scheme of te GALAN electrode boiler to the ascension pipe:
1. GALAN electrode boiler;
2. Ball faucet;
3. Circulating pump ;
4. Filter;
5. Blow valve;
6. Expansion tank;
7. Automatic equipment;
8. Air-inlet duct.


The connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler (principle)
1. GALAN electrode boiler;
2. Ball faucet;
3. Circulating pump ;
4. Filter;
5. Blow valve;
6. Expansion tank;
7. Automatic equipment;
8. Air-inlet duct.
The principle connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler:
Parallel connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler:
Parallel connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler
1. GALAN electrode boiler;
2. Ball faucet;
3. Circulating pump;
4. Filter;
5. Blow valve;
6. Expansion tank;
7. Automatic equipment;
8. Air-inlet duct;
9. Different heat source (gas, oil or solid-fired boiler)
The series connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler
The series connection scheme is good because it enables using of the solid-fired boiler (or gas boiler) and electrode boiler at the same time (or by turns). As you can see on the scheme: after heating, water comes from the electrode boiler to return pipe (with the help of the electrode boiler pump). And only then to the heating system directly. Whereby we don’t install additional circulating pump. The same happened with an expansion tank and safety group. There is also no need to buy and install it because they are inside the electrode boiler already. The blue pipe, which goes around the electrode boiler is designed to emergency shutdown of the electrode boiler followed by demounting in order to continue system working with the gas (solid-fired) boiler.
The difference from the parallel connection is that it is possible not to turn over one of the boilers. As far as with parallel connection, unless the gas boiler is turned over, hot water in electrode boiler will circulate through the small circle: from the gas boiler to electric one etc.
Operating scenario is the following :
You establish water temperature on a gas boiler - for example 50 degrees. And on an electrode boiler - 55 degrees and above, but only at night time. As night falls, the electrode boiler "understands" that the temperature is less than it was required, so it turns on and raises the coolant temperature to 55 degrees. It maintains the temperature till the morning, and then reduces temperature to 20 degrees (for example). All this time the gas boiler was pumping water through itself by the recycling pump, "thinking" that it happens by its service, that the water will not get cold and that gas burners are not switched on. In the morning the gas boiler sees that the temperature fell to 50 degrees as it was established and it gives the command to gas burners to turn on. This scenario is ideal with the interval meter. In this case economic effect will be noticeable.
Solid-fired boilers are even more simple in use. There is no need in setting the temperature, because it is regulated while burning the wood or coal (except modern solid-fired boilers with regulation of the air feeding damper). Simply said, solid-fired boiler works while wood or coal is burning. When wood is burnt, then an electrode boiler switches on.
There is one minus in this scheme. Absolutely all double-circuit gas boilers works on the following principle: when you start the hot water in order to wash hands or dishes, the gas boiler stops the the circulating pump work. The flow channel in the heating system stop working. An electrode boiler continue the coolant heating, but only from inside. Theoretically, the water termocontroller, installed in the electrode boiler will be activated. But it may not happen for some technical reason. In any event this variant is possible. What will happen then? The pressure in the system will jump and excessive water will start flow out from the relief valve of the gas boiler. Anyway, nothing good.
It is better not to open hot water while an electrode boiler is working. But it is the case of double-circle gas boilers. It will not happen with single-circuit and solid-fired boilers due to the absense of the second hot water circuit.
For starting-up the electrode boiler in the floor heating installation it is necesssary to prepare water In the followin way:
Start up the system and measure current at the return temperature 40 C
Boiler Peak current at 40 С
2 kW – 10 А
3 kW – 13 А
5 kW – 25 А
6 kW – 28 А
9 kW-220 V – 40 А
9 kW-380 V – 16 А
15 кW – 25 А
25 кW – 40 А
If at 40 degrees return temperature the current does not conform to the pointed in the table parameters,
proceed as follows:
1. If the current is less - it is needed to add gradually salting liquid (it reduces electrical resistivity of the liquid). First stage - no more than 1 teaspoon for 100 litres of water. If in 4 hours current increases slightly, it is necessary to repeat the first stage.
2. If the current is bigger - add distilled water (it increses electrical resistivity of the liquid). When water is prepared it is necessary to reduce the water temperature on the boiler outlet (sensor #2) to 40 degrees.
CAUTION!!!
While using an electrode boilers for heating the floors electric energy consumption increases meaningfully.
Connection scheme of the GALAN electrode boiler with the floor heating

1. GALAN electrode boiler;
2. Ball faucet;
3. Circulating pump;
4. Filter;
5. Blow valve;
6. Expansion tank;
7. Automatic equipment;
8. Air-inlet duct;
9. Bypass pipe;
10. Floor heating circuit;
11. Circuit engine;
12. Room thermostat.
Connection scheme of the GALAN elctrode boiler with the floor heating:


